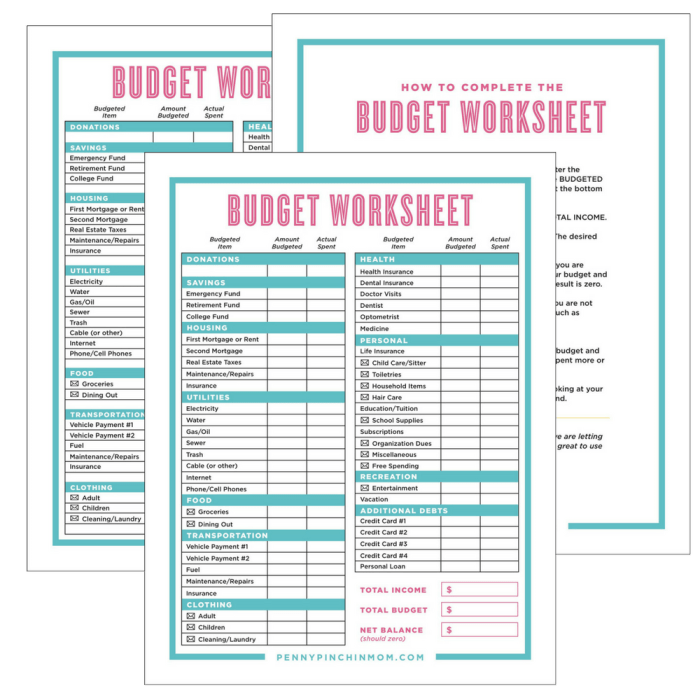
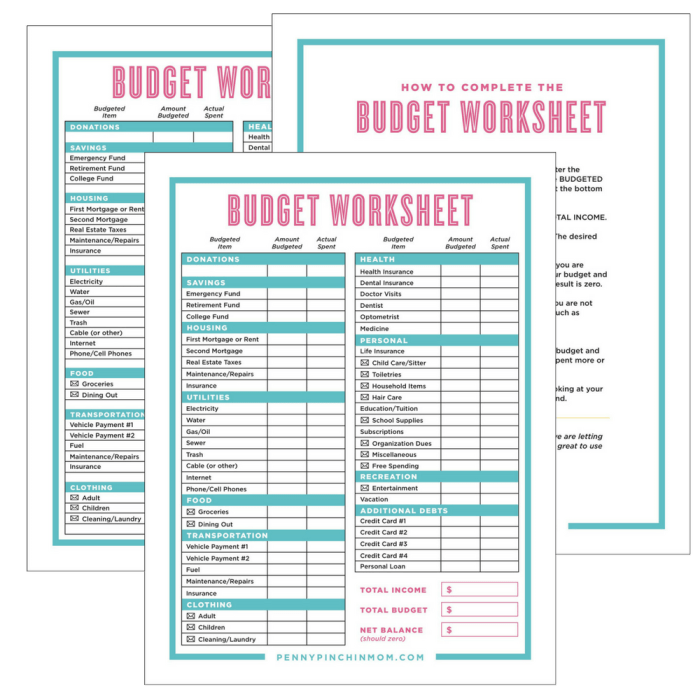
How to create a budget is a fundamental skill for anyone looking to take control of their finances. Whether you’re aiming to save for a dream vacation, pay off debt, or simply have more peace of mind about your money, a well-crafted budget can be your roadmap to financial success.
Creating a budget isn’t about deprivation; it’s about making informed choices about how you spend your money. By understanding your income, tracking your expenses, and setting realistic financial goals, you can gain a clear picture of your financial situation and empower yourself to make positive changes.
Setting Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is an essential step in creating a successful budget. Having specific financial objectives helps you stay motivated and track your progress. By setting goals, you can identify where your money is going, and make conscious decisions to achieve your desired financial outcomes.
Benefits of SMART Financial Goals, How to create a budget
SMART goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. These characteristics make financial goals more effective and actionable.
- Specific:Clearly define what you want to achieve. For example, instead of saying “I want to save more,” specify “I want to save $5,000 in the next year.”
- Measurable:Quantify your goal to track your progress. For example, “I want to reduce my debt by 20% in the next six months.”
- Achievable:Set realistic goals based on your current financial situation and income. For example, “I want to invest $100 per month in a retirement account.”
- Relevant:Ensure your goals align with your overall financial objectives and values. For example, “I want to save enough money to purchase a home in five years.”
- Time-bound:Set a deadline to provide a sense of urgency and motivation. For example, “I want to pay off my credit card debt by the end of the year.”
Sample Financial Goal Setting Worksheet
A financial goal setting worksheet can help you organize your financial aspirations and track your progress.
| Goal | Amount | Timeline | Action Steps | Progress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Save for a down payment on a house | $20,000 | 3 years | Increase monthly savings, explore investment options | $5,000 saved so far |
| Pay off student loan debt | $15,000 | 2 years | Make extra payments, consider debt consolidation | $8,000 paid off |
| Save for retirement | $100,000 | 15 years | Contribute regularly to a 401(k) or IRA | $25,000 saved |
Examples of Short-Term and Long-Term Financial Goals
Financial goals can be categorized as short-term or long-term based on their timeframe.
Short-Term Financial Goals
Short-term goals typically have a timeframe of less than a year.
- Save for a vacation:This goal could be achieved within a few months, depending on the cost of the trip.
- Pay off a small debt:This could be a credit card balance or a small personal loan.
- Build an emergency fund:Aim to have three to six months of living expenses saved in case of unexpected events.
Long-Term Financial Goals
Long-term goals have a timeframe of more than a year.
- Purchase a home:This goal may require several years of saving and planning.
- Save for retirement:This is a long-term goal that requires consistent saving and investing over many years.
- Fund your children’s education:This goal may involve saving for college or other educational expenses.
Creating a Budget Plan

A budget plan is a roadmap that helps you manage your finances effectively. It Artikels how you will allocate your income to different spending categories and track your progress towards your financial goals.
Steps Involved in Creating a Budget Plan
To create a budget plan, you need to follow these steps:
- Track your income and expenses.This involves recording all sources of income and all expenses for a period of time, typically one month. This will give you a clear picture of your financial situation.
- Categorize your expenses.Once you have tracked your expenses, categorize them into different groups, such as housing, food, transportation, entertainment, and debt payments. This will help you identify areas where you can cut back or save more.
- Set a budget for each category.After categorizing your expenses, you can allocate a specific amount of money to each category based on your priorities and financial goals. You can use a budget template or spreadsheet to help you with this process.
- Monitor your progress and make adjustments.Once you have created your budget, it’s important to monitor your progress regularly and make adjustments as needed. You may need to adjust your spending in certain categories or find ways to increase your income to reach your financial goals.
Budget Templates and Tools
There are various budget templates and tools available online and in budgeting apps. These resources can help you streamline the budgeting process.
- Spreadsheet templates:These are simple and customizable, allowing you to track your income and expenses in a structured format. Popular options include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and OpenOffice Calc.
- Budgeting apps:These apps offer features like automatic expense tracking, budgeting categories, and financial goal setting. Some popular budgeting apps include Mint, Personal Capital, and YNAB (You Need a Budget).
Allocating Funds to Different Categories
When allocating funds to different categories, it’s important to consider your individual needs and priorities.
- Needs vs. Wants:Differentiate between essential needs, such as housing, food, and utilities, and non-essential wants, such as entertainment and dining out. Allocate a larger portion of your budget to needs and prioritize saving for future goals.
- The 50/30/20 Rule:This is a popular budgeting rule that suggests allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment. However, you can adjust these percentages based on your individual circumstances and financial goals.
- Zero-Based Budgeting:This method involves allocating every dollar of your income to a specific category, leaving no room for unplanned spending. It can be helpful for those who struggle with overspending.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Budget
Creating a budget is only the first step towards achieving your financial goals. Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential to ensure your budget remains effective and aligns with your evolving needs and circumstances.
Regular Budget Reviews
Regularly reviewing your budget allows you to track your progress, identify areas where you’re overspending or underspending, and make necessary adjustments.
- Monthly Reviews:A monthly review is ideal for staying on top of your spending habits and ensuring you’re on track to meet your financial goals. This allows you to address any issues promptly.
- Quarterly Reviews:Quarterly reviews offer a broader perspective on your spending patterns and allow you to assess your overall financial health. They are particularly helpful for identifying long-term trends and making necessary adjustments to your budget.
- Annual Reviews:An annual review is crucial for evaluating your budget’s effectiveness in the context of your financial goals. It allows you to make significant adjustments based on changes in your income, expenses, or financial priorities.
Identifying and Addressing Budget Discrepancies
During your budget reviews, you may discover discrepancies between your planned spending and actual spending. These discrepancies can arise from various factors, such as unexpected expenses, overspending in specific categories, or inaccurate tracking of income and expenses.
- Track Your Spending:Use a budgeting app, spreadsheet, or notebook to diligently track your income and expenses. This allows you to identify areas where you’re overspending and make necessary adjustments.
- Analyze Spending Patterns:Analyze your spending patterns to identify recurring expenses that may be exceeding your budget. This can help you pinpoint areas where you can cut back or find more affordable alternatives.
- Categorize Expenses:Categorizing your expenses can provide valuable insights into your spending habits. For example, you might realize you’re spending more on entertainment than you initially planned.
Adjusting Your Budget Based on Changing Circumstances
Life is unpredictable, and your financial circumstances can change over time. It’s essential to adjust your budget accordingly to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
- Income Changes:If your income increases, you can adjust your budget to allocate more funds towards savings, debt repayment, or other financial goals. Conversely, if your income decreases, you may need to cut back on discretionary spending to maintain financial stability.
- Expense Changes:Changes in expenses, such as a new car payment or rising housing costs, may require adjustments to your budget. You may need to prioritize essential expenses and cut back on discretionary spending to accommodate these changes.
- Financial Goals:As your financial goals evolve, your budget may need to be adjusted to reflect these changes. For example, if you decide to buy a house, you may need to increase your savings rate or adjust your spending habits to accumulate a down payment.
Budgeting Tips and Strategies: How To Create A Budget
Creating a budget is a crucial step towards achieving your financial goals. But simply having a budget isn’t enough; you need to implement effective strategies to make it work. This section will explore valuable tips and strategies to help you manage your budget effectively and reach your financial objectives.
Budgeting Tips and Strategies
Budgeting tips and strategies can significantly impact your financial well-being. These techniques can help you save money, reduce debt, and achieve your financial goals. Here are some helpful tips and strategies:
Track Your Spending
Tracking your spending is the first step to creating a budget. This allows you to understand where your money is going and identify areas where you can cut back. There are various methods to track your spending, including:
- Using a spreadsheet:You can create a simple spreadsheet to track your income and expenses manually.
- Using budgeting apps:Several budgeting apps are available to track your spending automatically, categorize your expenses, and provide insights into your financial behavior.
- Using a budgeting journal:A budgeting journal allows you to record your expenses manually, providing a tangible record of your spending habits.
Prioritize Your Needs and Wants
After tracking your spending, it’s essential to distinguish between your needs and wants. This allows you to allocate your budget effectively and prioritize essential expenses over discretionary spending.
- Needs:These are expenses essential for survival, such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare.
- Wants:These are expenses that are not essential for survival but add comfort and enjoyment to your life, such as entertainment, dining out, and vacations.
Set Realistic Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is essential for staying motivated and on track. When setting goals, consider factors such as your income, expenses, and financial obligations. It’s also crucial to break down large goals into smaller, more manageable steps to make them seem less daunting.
Create a Savings Plan
Saving money is essential for achieving your financial goals, whether it’s for retirement, a down payment on a house, or a dream vacation. Creating a savings plan helps you allocate a specific amount of money regularly towards your savings goals.
- Automate your savings:Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account to ensure you’re saving regularly.
- Use a high-yield savings account:Explore high-yield savings accounts that offer higher interest rates to maximize your savings growth.
Review and Adjust Your Budget Regularly
Your financial situation can change over time, so it’s crucial to review and adjust your budget regularly. This ensures your budget remains relevant and effective in meeting your current financial needs and goals.
- Review your budget at least once a quarter:Regularly review your budget to assess your spending habits and identify areas where you can make adjustments.
- Adjust your budget as needed:If your income or expenses change, update your budget to reflect these changes.
Resources for Further Budgeting Education
There are numerous resources available to help you learn more about budgeting and financial management. These resources can provide valuable insights and guidance to improve your financial literacy.
- Personal finance websites:Many websites offer valuable information on budgeting, saving, investing, and other personal finance topics. Some popular websites include NerdWallet, Investopedia, and Bankrate.
- Financial books and articles:Numerous books and articles are available on personal finance topics, providing in-depth knowledge and practical tips for managing your money.
- Financial advisors:A financial advisor can provide personalized advice and guidance on creating a budget, investing, and achieving your financial goals.
- Community organizations:Many community organizations offer free or low-cost financial literacy programs and workshops.
Budgeting Apps and Software
Budgeting apps and software can help you track your spending, create budgets, and analyze your financial data. They can automate many aspects of budgeting, making it easier to manage your finances.
- Mint:Mint is a popular budgeting app that allows you to track your spending, create budgets, and set financial goals. It automatically aggregates your accounts and provides insights into your spending habits.
- YNAB (You Need a Budget):YNAB is a budgeting app that emphasizes the importance of zero-based budgeting, where you allocate every dollar of your income to a specific purpose. It helps you prioritize your spending and track your progress towards your financial goals.
- Personal Capital:Personal Capital is a financial management platform that offers budgeting tools, investment tracking, and retirement planning assistance. It provides a comprehensive overview of your finances and helps you make informed financial decisions.
Outcome Summary
Creating a budget is a journey, not a destination. It’s an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment as your circumstances change. Remember, the key is to find a system that works for you, embrace flexibility, and celebrate your progress along the way.
By taking the time to understand your finances, set goals, and create a budget, you’ll be well on your way to achieving financial stability and reaching your financial aspirations.
Q&A
How often should I review my budget?
It’s recommended to review your budget at least once a month to ensure it’s still aligned with your goals and spending habits.
What if I can’t stick to my budget?
Don’t get discouraged! If you find yourself consistently overspending, try to identify the root cause and make adjustments. Consider using a budgeting app or talking to a financial advisor for additional support.
Is it okay to have a negative balance in my budget?
It’s not ideal to have a negative balance, but it can happen. If you’re in this situation, try to find ways to reduce expenses or increase income to get back on track.